Difference between high-speed steel vs high carbon steel
The price of high carbon steel is cheap, the hardness of high-speed steel is higher, and the wear resistance of high-speed steel is better. High speed steel is used for […]
The price of high carbon steel is cheap, the hardness of high-speed steel is higher, and the wear resistance of high-speed steel is better. High speed steel is used for mold steel.
In modern industrial production, material selection plays a crucial role in determining product performance. High-speed steel (HSS) and high-carbon steel, both widely used in tool manufacturing, exhibit distinct characteristics and applications. Let’s delve into their properties, applications, hardness, wear resistance, price, and advantages and disadvantages.
Our factory business: carbide parts, mold parts, medical injection molds, precision injection molds, teflon PFA injection molding, PFA tube fittings. email: [email protected],whatsapp:+8613302615729.
I. Definitions and Properties
High-Speed Steel Overview.
High-speed steel, also known as tool steel or white steel, is a high-carbon, high-alloy ledeburitic steel. It features high hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance, making it ideal for complex thin-blade cutting tools and high-temperature bearings.
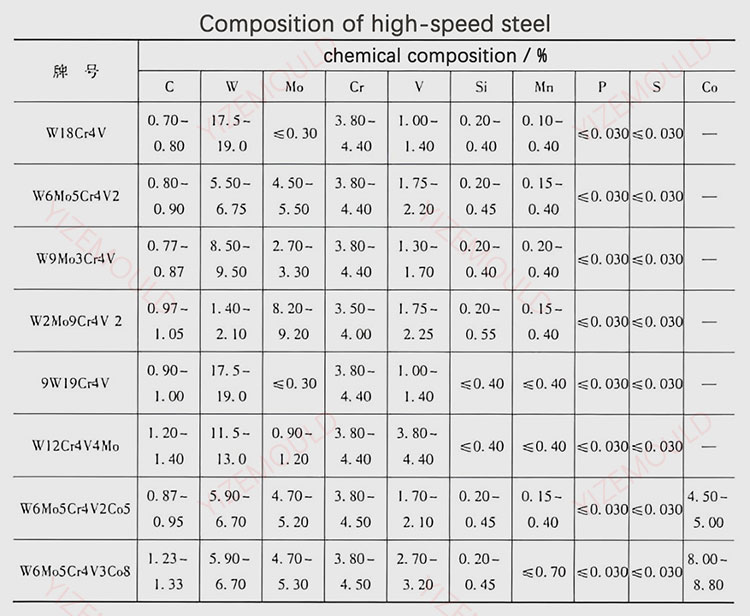
High-Carbon Steel.
High-carbon steel contains a higher carbon content, resulting in high strength and hardness after heat treatment. It is suitable for manufacturing springs and wear-resistant parts, but its weldability and cold plastic deformation ability are relatively poor.
II. Chemical Composition and Heat Treatment
High-Speed Steel Composition and Heat Treatment.
HSS is rich in alloying elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, and chromium. It undergoes specific heat treatment processes like high-temperature annealing, quenching, and high-temperature tempering to achieve its superior properties.
High-Carbon Steel Composition and Heat Treatment.
High-carbon steel has a significantly higher carbon content than HSS and typically requires complex heat treatment processes like annealing, normalizing, tempering, and quenching to achieve the desired hardness and toughness.
III. Performance Comparison
Hardness.
- High-carbon steel possesses high hardness, typically around 60-65 HRC, but not as high as HSS.
- HSS exhibits hardness reaching 65-70 HRC and maintains stability even at high temperatures.

Wear Resistance.
- High-carbon steel has relatively poor wear resistance and is prone to wear and cracking.
- HSS demonstrates excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for high-speed and high-load applications.
IV. Applications
HSS, with its superior hardness, toughness, and wear resistance, is primarily used for cutting tools, mold steel, and high-speed bearings, such as drills and milling cutters. High-carbon steel, on the other hand, is commonly used for manufacturing springs and wear-resistant parts.
V. Price Comparison
High-carbon steel is relatively common and affordable. In contrast, HSS is more expensive due to its specialized properties and is typically used in more demanding and professional industrial applications.
Conclusion
Both HSS and high-carbon steel have their own advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different industrial applications. When choosing the appropriate material, engineers need to consider the specific working conditions and performance requirements to make informed decisions.
Related articles:






